TL;DR: Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) in 2026
- GEO is the discipline of making your content the preferred source for AI answers in ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, Claude, Copilot, and other AI assistants.
- Research from the original GEO paper shows that adding authoritative quotes, statistics, and citations can raise AI answer visibility by roughly 30–40% on benchmarked queries.
- Industry case studies report that AI‑referred visitors often convert 2–25× better than classic organic search traffic, especially on high‑intent B2B queries.
- GEO builds on SEO fundamentals (crawlability, E‑E‑A‑T, technical hygiene) but optimizes for citations and share of voice inside AI responses rather than just blue‑link rankings.
- This guide gives you a step‑by‑step roadmap: content architecture, schema, llms.txt, crawler settings, and measurement so you can turn AI answers into a repeatable acquisition channel.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of optimizing digital content to increase its likelihood of being cited, quoted, and synthesized by large language models and AI-powered search engines. Unlike traditional SEO, which focuses on ranking in search engine results pages to drive clicks, GEO targets citation and mention rates within AI-generated answers that users receive directly without clicking through to websites.
The term was formally introduced in November 2023 by researchers Pranjal Aggarwal, Vishvak Murahari, and colleagues from Princeton University, Georgia Tech, the Allen Institute for AI, and IIT Delhi. Their groundbreaking paper, presented at the ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining in August 2024, established both the GEO framework and GEO-bench—a benchmark containing 10,000 diverse queries for testing optimization strategies.
The shift from traditional search to generative AI represents a fundamental transformation in how users discover information. While Google and Bing present ranked lists of pages for users to explore, generative engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews synthesize information into direct answers with inline citations. This changes the optimization goal from “rank higher” to “become citation-worthy.”
Why does GEO matter for brands in 2026?
The AI search landscape is experiencing explosive growth. According to the AI Search Industry Report 2025, Google’s AI Overviews now reach 1.5 billion monthly users across 200 countries, making it the largest generative AI deployment globally. AI referrals to websites increased 357% year-over-year to the top 1,000 websites globally in June 2025 compared with June 2024, generating over 1.13 billion referrals.
As Rand Fishkin, founder of SparkToro, explains: “We’re witnessing a transition from the ‘ten blue links’ model of search to what we might call ‘direct answer engines’—systems that synthesize information from multiple sources to provide complete responses. This doesn’t just change how search works; it changes how brands need to approach visibility altogether.”
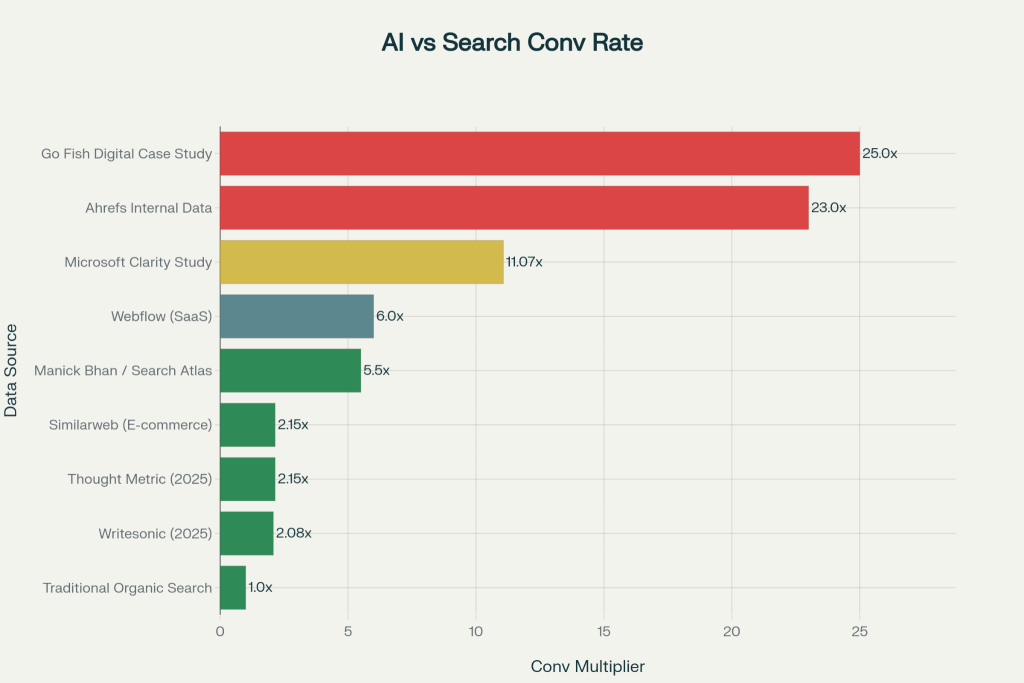
Organizations implementing GEO strategies report remarkable results. Research from 2025 shows AI-referred traffic converts significantly higher than traditional organic search—though the magnitude varies by platform, metric, and industry.
Go Fish Digital’s case study documented the highest conversion advantage at 25X higher conversion rates, achieving a 43% increase in AI-sourced traffic within 90 days with an 83.33% conversion rate improvement. Ahrefs’ internal data showed 23X higher conversion rates from AI referrals, with AI visitors representing 12.1% of signups despite being only 0.5% of traffic.
More conservative industry benchmarks show a consistent range: Writesonic documented 2.08X improvements, Similarweb found 2.15X, Webflow reported 6X advantages, and Microsoft Clarity’s study across 1,200 publishers documented 11.07X improvements for subscription conversions. Across all sources, AI-referred traffic consistently outperforms traditional organic search by 2-25X depending on conversion type, industry, and platform.
How is GEO different from traditional SEO?
GEO and SEO share the same technical foundations, but they optimize for different outcomes: SEO competes for ranked positions and clicks, while GEO competes for citations and narrative control inside AI‑generated answers.
As Neil Patel explains in his comprehensive GEO guide, there is substantial overlap in technical requirements between SEO and GEO. Research shows up to 87% overlap between sources cited by AI systems and top Google/Bing organic results. However, meaningful differentiation requires understanding how AI systems evaluate and extract information differently from traditional ranking algorithms.
“Good SEO is good GEO.” — Danny Sullivan, Director at Google Search
As he elaborated at WordCamp US 2025, the fundamental principles remain unchanged: creating valuable, user-focused content with strong E-E-A-T signals works for both traditional search engines and AI-powered responses. The basic things have not changed, and SEO fundamentals remain foundational to GEO success.
Which GEO techniques are proven to increase AI citations?
Experiments on the GEO‑bench dataset show that specific, content‑level changes can significantly increase how often AI systems pull and cite your pages in generated answers.
The Princeton/Georgia Tech study tested nine distinct optimization methods using the GEO-bench benchmark, providing the first empirical evidence of what improves AI visibility.
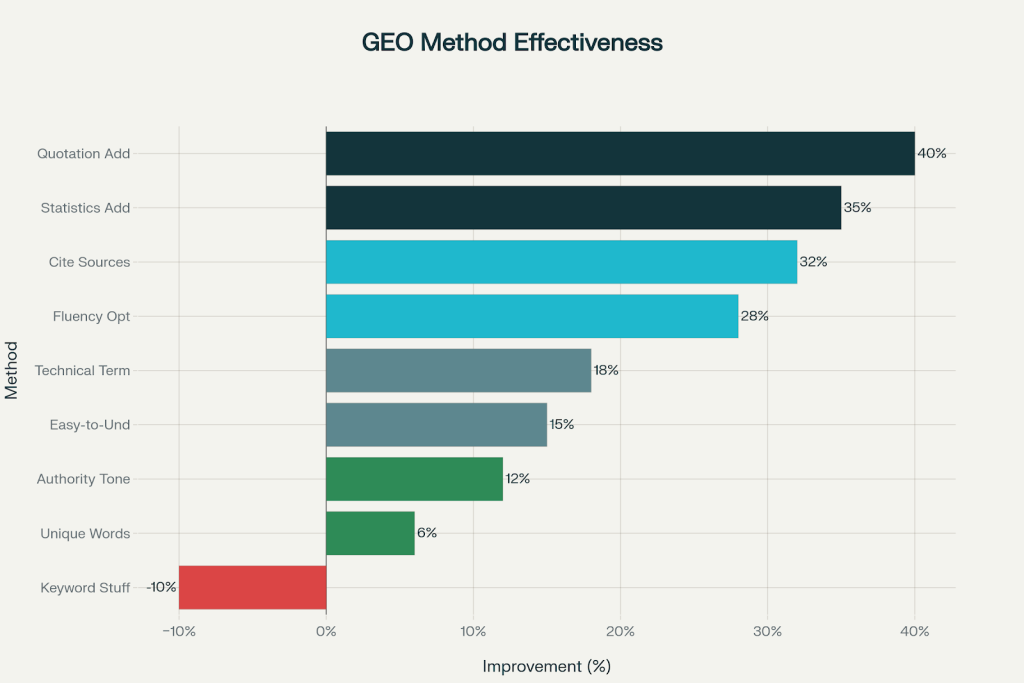
Top‑performing techniques
- Add authoritative quotations. Incorporate short, well‑attributed quotes from recognized experts (researchers, founders, industry leaders) to provide ready‑made snippets that AI models can reuse; this was the single best‑performing intervention in the GEO study.
- Embed statistics and concrete numbers. Replace vague statements with specific metrics, timelines, percentages, and comparisons; AI engines favor content that reduces ambiguity and supports data‑driven answers.
- Cite high‑authority external sources. Link out to reputable research, standards bodies, and official data (e.g., .gov, .edu, industry reports) to give models verifiable grounding paths.
- Improve fluency and structure. Use clear headings, short paragraphs, and consistent hierarchy (H1 → H2 → H3) so AI systems can reliably map sections to user questions and extract coherent chunks.
Techniques to avoid
- Do not rely on keyword stuffing. Repeating phrases unnaturally reduced AI visibility in controlled tests and conflicts with how modern models score content quality.
How do different AI platforms (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google, Claude, Copilot) treat your content?
Different AI platforms employ distinct mechanisms for retrieving and citing information, requiring tailored optimization approaches.
How can you optimize for ChatGPT?
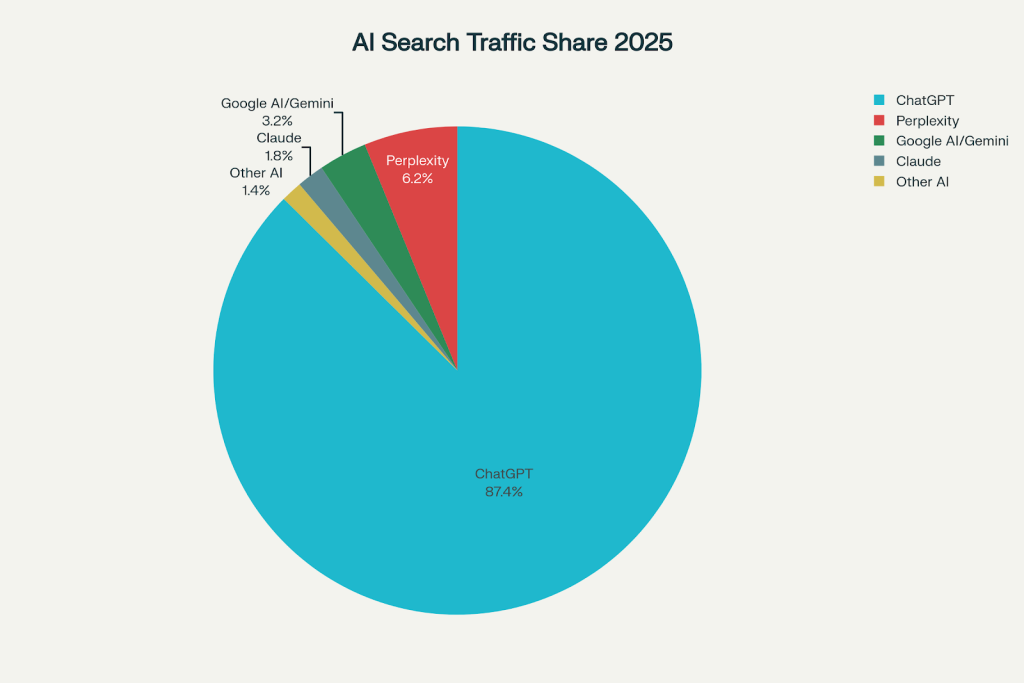
Recent datasets show ChatGPT currently drives around 80% of AI chatbot referrals to websites, with some industry benchmarks observing shares as high as roughly 87% in specific samples. The platform uses Bing as its underlying search infrastructure and analyzes approximately 12 search results to synthesize answers. ChatGPT heavily favors long-form content (2,000+ words), detailed explanations with definitions, and data-driven analysis. The platform orders references from newest to oldest, making content freshness particularly important. For local queries, ChatGPT references Google Maps data significantly, making Google Business Profile optimization relevant for visibility.
How can you optimize for Perplexity?
Perplexity operates as the most citation-intensive platform, including numbered inline references with every response. The platform favors conversational tone, user experiences, Q&A format content, and recently updated information. Critically, Perplexity prefers authentic voices from Reddit and forums over corporate marketing copy. The platform draws from a “small list of trusted sites” and requires PerplexityBot and BingPreview crawlers to be allowed in robots.txt.
How can you optimize for Google AI Overviews?
Google AI Overviews now appear on approximately 13% of all search results, with 46% overlap between AIO citations and top 10 organic rankings in recent third‑party studies. A Google patent reveals a multi-stage document selection process evaluating positional ranking, click-through rates, trustworthiness (E-E-A-T signals), freshness, and content diversity. Content in the top 2 SERP positions has over 53% probability of AIO inclusion, making traditional SEO fundamentals essential for Google GEO. Research from Ahrefs shows that 76% of AI Overview citations pull from top-10 ranking pages, though only 17% of pages ranking #1-3 in traditional search appear in AI Overviews.
How can you optimize for Claude and Microsoft Copilot?
Claude distinguishes itself by using Brave Search rather than Google or Bing for its underlying search infrastructure. This means content must be indexed in Brave Search for Claude visibility—an often-overlooked requirement. Microsoft Copilot is deeply integrated with Bing and the Microsoft ecosystem, making LinkedIn articles, GitHub content, and Microsoft-indexed resources particularly valuable. Schema markup carries heavier weight in Copilot citations than other platforms.
What technical foundations are required for GEO (schema, crawlers, llms.txt, rendering)?
How should you approach schema and structured data for GEO?
Schema markup has evolved from an SEO enhancement to a critical component for AI search optimization. Microsoft confirmed using structured data to support LLM interpretation, and Google’s schema markup plays a critical role in grounding generative AI systems. A 2023 Data.world study found that enterprise knowledge graphs improved LLM response accuracy by up to 300%.
As Dr. Andreas Wichert, AI Researcher and Professor at Universidade de Lisboa, explains:
“GEO bridges the gap between static content and conversational AI. It’s about making information not just searchable, but understandable and actionable for machines.”
FAQPage schema enables direct answer extraction by mapping questions to accepted answers, making it easy for AI systems to pull exact responses. Research indicates that FAQ blocks with proper structured data implementation can increase website visibility in AI search results by up to 44%.
Article schema establishes freshness and authority signals by defining author, datePublished, headline, and publisher information.
HowTo schema optimizes procedural content with sequential, clear steps that AI can present directly to users.
Implementation best practices include focusing on 1-2 relevant schema types per page rather than excessive markup, using JSON-LD format (Google’s recommendation), ensuring schema reflects only what’s actually visible on the page, and connecting schema types semantically to create the “knowledge graph” structure AI systems prefer.
How should this page use schema for GEO?
This specific GEO guide should use a focused schema stack so AI systems can treat it as a canonical, well‑attributed reference when composing answers.
- Add
Articleschema with fields likeheadline,description,author,publisher,datePublished, anddateModifiedto clearly expose who wrote this guide and when it was last updated. - Link your brand using
Organizationschema (and reference it from the article viapublisher), includingname,url,logo, andsameAslinks to your main social and profile pages so assistants can reliably tie this content to your company entity. - Implement a compact
FAQPageblock with 6–10 of the strongest questions already covered in this article (for example, “What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?”, “How is GEO different from traditional SEO?”, “Which GEO techniques are proven to increase AI citations?”, and “Which metrics and tools should you use to measure GEO success?”) and concise, 40–80 word answers that mirror your on‑page content. - Serve all schema as JSON‑LD, ensure it only describes content that is actually visible on the page, and validate it with Google’s Rich Results Test before or right after publishing.
How should you configure crawler access for AI engines?
Effective GEO requires explicit crawler configuration for major AI platforms. The primary crawlers include GPTBot (OpenAI training), OAI-SearchBot (ChatGPT search), ClaudeBot (Anthropic), PerplexityBot, and Google-Extended (Gemini training). Current Cloudflare data shows GPTBot makes 569 million monthly requests and is blocked by only 5.89% of sites, indicating most organizations have not yet optimized crawler access.
A critical distinction exists between training crawlers (which train future model versions) and search crawlers (which power real-time search features). Blocking training does not necessarily block search visibility, allowing organizations to prevent their content from being used in model training while still appearing in AI search results.
What is llms.txt and how should you use it?
The llms.txt specification, proposed by Jeremy Howard in September 2024, provides a dedicated file for AI consumption at yoursite.com/llms.txt. This Markdown-formatted file summarizes key site content, important pages, and organizational information specifically for LLM parsing. While not universally adopted, ChatGPT has been observed fetching llms-full.txt files, and platforms including Wix and Yoast SEO now auto-generate these files.
Unlike robots.txt which controls crawler access, llms.txt acts as a “treasure map” helping AI find the right content to cite. Implementation involves creating both llms.txt (concise table of contents) and llms-full.txt (detailed content) files, maintaining clean semantic HTML with proper heading hierarchy, and ensuring stable, human-readable URLs.
How should you handle JavaScript rendering for GEO?
Most AI crawlers cannot execute JavaScript like traditional search engine crawlers, meaning content rendered via client-side JavaScript is invisible to AI systems. Organizations using React, Angular, or Vue must implement server-side rendering (SSR) or static site generation (SSG) to ensure content appears in the initial HTML source. Testing is straightforward: view page source in a browser—if main content isn’t visible, AI crawlers won’t see it.
How should content be structured for maximum AI extractability?
AI systems reward clarity over keyword density, and content must be formatted for “extractability”—making it effortless for AI systems to lift insights and cite them properly.
Why does an answer-first structure matter for GEO?
Content should lead with a direct answer in the first 1-2 sentences (40-60 words), followed by supporting context, then detailed explanation. This structure aligns with how generative engines construct responses—they need immediate, clear answers that can be quoted or paraphrased, with depth available for more complex queries. Organizations that implement answer-first formatting report significantly higher citation rates.
How should you modularize content for AI extractability?
Create self-contained, citable sections with clear headings and concise paragraphs. Short paragraphs of 2-4 sentences with one idea per paragraph prevent AI extraction failures. Headings every 200-300 words with descriptive text (not generic labels like “Introduction”) enable section-level indexing. Tables for comparisons, bullet points for key information, and clear definition blocks make content modular and extractable.
How should you design headings for AI-style questions?
Use H2/H3 as real questions that mirror how users query AI systems. This creates natural extraction points for AI platforms that match specific user intents. For example, instead of “Benefits” as a heading, use “What are the main benefits of GEO for B2B companies?” This approach significantly increases the likelihood of your content being selected for question-answering queries.
How do E‑E‑A‑T and digital PR influence GEO performance?
Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) have evolved from SEO best practices to primary citation factors in GEO. As outlined in Google’s helpful content guidelines, as AI systems compress sources into single responses, models rely on clear signals to decide which pages shape the final output.
How can you demonstrate experience and expertise for GEO?
Experience signals require demonstrating first-hand knowledge through case studies, original research, and real-world examples. Organizations that map answers back to named experts and disclose AI involvement saw 12-15% increases in session duration. Expertise involves associating content with credentialed subject-matter experts through Person schema with credentials, job titles, and links to professional profiles, visible author bios with demonstrated expertise, and clear evidence of qualifications.
How can you build authoritativeness and trust for GEO?
Authoritativeness is built through third-party mentions, industry recognition, and consistent publishing history. A 2025 arXiv study found AI search shows “systematic and overwhelming bias towards earned media (third-party, authoritative sources) over brand-owned and social content.” This means coverage in authoritative publications, presence on review platforms like G2, active participation on Reddit and industry forums, and backlinks from trusted domains all influence AI visibility beyond direct content optimization.
New research from SE Ranking analyzing 129,000 unique domains revealed that referring domains ranked as the single strongest predictor of ChatGPT citations. Sites with over 350,000 referring domains averaged 8.4 citations, while those with fewer than 2,500 averaged only 1.6-1.8 citations. Sites scoring 97-100 on domain trust metrics averaged 8.4 citations compared to 1.6 for sites below 43.
How does third-party validation impact GEO?
Branded web mentions show the strongest correlation with visibility in AI Overviews, significantly outperforming traditional backlinks. As The HOTH explores in their digital PR guide, brands earning the most web mentions appear in up to 10 times more AI Overviews than those in the next closest quartile. Google has confirmed that AI systems identify trustworthy information by recognizing reputable mentions, citations, and content consistency.
How can topical authority and clusters strengthen GEO?
AI search engines prioritize brands that demonstrate expertise across entire subjects, not just individual pages. The pillar-and-cluster architecture creates a web of authority that signals comprehensive topic ownership.
A comprehensive hub page provides overview and deep-dive content on a core topic, supported by cluster pages covering specific subtopics with internal links back to the pillar. This structure helps both users and AI systems understand relationships between content pieces, reinforcing topical coverage. For example, a pillar page on “Content Marketing Strategy” might link to cluster pages on “Email Marketing Best Practices,” “Social Media Content Calendar,” “SEO Content Optimization,” and “Content Performance Analytics.”
Research demonstrates that sites with strong topic cluster structures see higher citation rates as AI systems recognize comprehensive coverage and can pull information from multiple related pages to construct more complete answers.
Which metrics and tools should you use to measure GEO success?
GEO replaces keyword‑only tracking with a mix of citation, visibility, and conversion metrics tied to how often AI assistants surface and send traffic to your brand.
What core metrics define GEO success?
- AI citation rate: Percentage of sampled AI answers for a query set that reference your domain at least once. Track separately by platform (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, Claude, Copilot).
- AI share of voice: Proportion of all citations across competitors that mention your brand for a topic or cluster (e.g., 30%+ SoV on “GEO for B2B SaaS”).
- AI referral traffic and conversions: Sessions and conversions attributed to AI assistants in analytics, compared side‑by‑side with classic organic; many brands see 2–25× higher conversion rates from AI‑referred visitors.
- Answer quality and sentiment: Qualitative review of how accurately and favorably AI systems describe your products, pricing, and positioning, especially on evaluative and comparison queries.
How often should you measure GEO performance?
- Run a monthly AI visibility audit on your priority query set across major assistants, log citation counts and SoV, and compare against the previous month.
- Review AI‑referred performance in analytics each month (traffic, signup, opportunity, revenue) to justify or adjust GEO investments.
Which tools and platforms support GEO measurement?
The GEO tools landscape has rapidly matured since 2024. Enterprise platforms like Conductor, Semrush AI Visibility Toolkit, Profound, and AthenaHQ offer comprehensive visibility monitoring, optimization recommendations, and hallucination detection. Pricing typically starts at $495/month for entry-level enterprise plans.
Mid-market solutions including Otterly.AI ($49/month), Peec AI (€89/month), and Geoptie provide brand visibility tracking and competitive benchmarking for smaller organizations. Free diagnostic tools like Mangools AI Search Grader and HubSpot AI Search Grader offer starting points for visibility assessment.
Google Analytics 4 can track AI referral traffic with custom configuration using regex patterns to identify sources: (.*chatgpt.com.*|.*perplexity.*|.*copilot.microsoft.com.*|.*claude.ai.*). However, attribution remains imperfect—ChatGPT often masks origin as “Direct” traffic, and some AI platforms inconsistently pass referrer headers. Manual monitoring by regularly querying target phrases across AI platforms remains essential for comprehensive visibility tracking.
What real-world results can GEO deliver?
Across all sources, AI‑referred traffic consistently outperforms traditional organic search by 2–25× depending on conversion type, industry, and platform, with the upper end of that range coming from very high‑intent funnels.
Go Fish Digital
Go Fish Digital’s self-study demonstrated the commercial viability of GEO implementation. Within 90 days, they achieved 10% of organic traffic from generative engines. AI-sourced traffic showed 27% conversion to Sales Qualified Leads compared to standard organic traffic. Session duration was 30% longer for LLM-sourced visitors versus Google, and conversion rates were 25 times higher from AI referrals.
LS Building Products
According to Maximuslabs case studies and Single Grain’s analysis, LS Building Products implemented comprehensive GEO strategies focusing on content architecture and schema markup. Working with Single Grain Marketing, results included a 67% increase in organic traffic, 540% boost in Google AI Overviews mentions, and substantial improvements in brand visibility across multiple AI platforms. The company rebuilt content architecture around AI-friendly structures with clear answer blocks, comprehensive FAQ sections, and detailed product specifications. The traffic value added from AI visibility alone exceeded $400,000 in annual advertising equivalent.
Smart Rent
Smart Rent’s property management software case study showed a 32% increase in sales-qualified leads within six weeks of implementing their AI-native SEO approach. Their sales team reported that prospects arriving from ChatGPT and Claude citations were 3X more likely to complete onboarding than those from traditional channels, and prospects moved through the pipeline 40% faster.
Emichi
We are currently conducting internal research on our own website, emichi.co, to rigorously test the Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) principles outlined in this guide. This article—”Generative Engine Optimization: The Complete Guide to AI Search Visibility in 2026″—is the first piece of content to be fully optimized for GEO to measure empirical results, specifically tracking AI referral traffic volume and conversion performance. The full case study and results will be published upon completion of the initial tracking period.
What implementation roadmap should teams follow to adopt GEO?
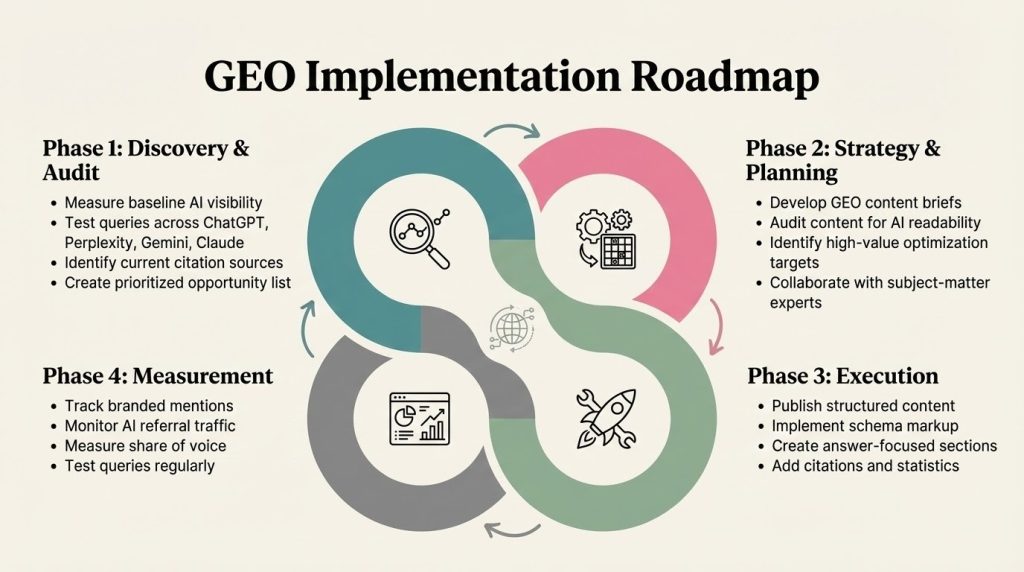
Phase 1: Discovery & Audit
Begin by measuring baseline AI visibility across major platforms. Test brand queries, product names, and key topics across ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, Gemini, and Claude. Document where your content is currently cited, how competitors appear in responses, and gaps in your AI visibility. Create a prioritized opportunity list focusing on high-value queries with commercial intent, topics where you have strong expertise but low visibility, and content that’s already performing well in traditional search but missing from AI responses.
Phase 2: Content Strategy & Planning
Develop GEO-specific content briefs that incorporate answer-first structure, schema markup requirements, and citation strategies. Audit existing content for AI readability by checking heading structure, paragraph length, extractability, and presence of statistics and quotes. Identify high-value content for optimization, prioritizing pages with existing traffic but no AI citations, cornerstone content representing your core expertise, and conversion-focused pages. Collaborate with subject-matter experts to add authentic expertise signals through author bios, expert quotes, and original insights.
Phase 3: Execution
Publish semantically structured content with clear H1-H2-H3 hierarchy and question-based headings. Implement schema.org markup focusing on FAQPage, Article, and HowTo schemas. Create answer-focused sections that lead with direct responses in the first 1-2 sentences. Add citations to authoritative sources, embed relevant statistics with attribution, and incorporate expert quotations. Ensure technical requirements are met including AI crawler access, server-side rendering for JavaScript frameworks, and llms.txt implementation.
Phase 4: Measurement & Iteration
Track branded mentions daily across AI platforms using manual queries or automated monitoring tools. Monitor AI referral traffic in Google Analytics with proper source attribution. Measure share of voice weekly by testing priority queries and comparing your visibility to competitors. Conduct monthly performance reviews analyzing which content types receive most citations, which platforms drive highest-quality traffic, and how AI traffic converts compared to traditional organic search. Iterate based on data by refreshing top-performing content with new statistics, expanding coverage of high-citation topics, and replicating successful content patterns.
What strategic recommendations and quick wins should you prioritize?
Quick Wins for Immediate Impact
Organizations can implement several high-impact tactics within the first 30 days.
- Add TL;DR sections to the beginning of existing long-form content summarizing key points in 3-5 bullet points.
- Implement FAQPage schema on your most important pages, focusing on questions users actually ask.
- Update author bios with credentials, expertise markers, and links to professional profiles.
- Add original statistics by conducting simple surveys, analyzing proprietary data, or creating visual comparisons.
- Structure content with clear headers every 200-300 words and 2-4 sentence paragraphs.
- Test brand queries across major AI platforms weekly to establish baseline visibility and track improvements.
Integration, Not Replacement
GEO builds on SEO fundamentals rather than replacing them. The strategic approach involves maintaining traditional SEO investment while allocating incremental resources (typically 20-30% of total search budget) to GEO-specific initiatives. Organizations should continue core SEO activities including technical optimization, backlink building, and keyword research while adding GEO layers like schema markup enhancement, content restructuring for extractability, and AI crawler configuration.
Content Strategy Evolution
The content strategy must evolve from “ranking for keywords” to “becoming the answer.” This means comprehensive topic coverage through pillar-cluster architecture rather than thin keyword-targeted pages. Content should be structured for easy AI extraction with modular sections, clear answers, and supporting depth. Embed statistics and authoritative citations throughout to signal trustworthiness and provide verification trails. Build presence on platforms that inform AI training, particularly Reddit, industry forums, and authoritative publications.
What trends will shape the future of GEO?
According to Search Engine Land’s 2026 GEO planning guide, Gartner projects AI assistants will handle 25% of searches by 2026 and 50% by 2028, running alongside traditional engines for several years. The trajectory suggests AI search share could grow from under 1% currently to 5-10% of total web traffic through 2028. McKinsey projects $750 billion in US consumer spending will flow through AI-powered search by 2028.
As noted by Manick Bhan, Founder and CTO of Search Atlas:
“We’re seeing 5.5x higher conversion rates from ChatGPT referrals compared to Google organic search.”
RankTracker’s future predictions highlight emerging trends including social sentiment influence likely increasing in future AI models as platforms integrate more real-time signals from social media and community discussions. Multi-format content combining text with video, audio, and interactive elements is gaining preference as multimodal models mature. Real-time information is increasingly valued, with AI systems showing strong preference for recently published and regularly updated content. Domain-specific optimization is becoming more critical as AI systems develop specialized capabilities for different industries and query types.
Strategic budget allocation for 2026 GEO planning should consider approximately 40% for core SEO to maintain technical and content foundations, 25% for digital PR and E-E-A-T building authority and trust signals, 20% for data and reporting including entity tracking and attribution, 10% for training in cross-skill development, and 5% for innovation in new formats and AI-native content.
Conclusion
Generative Engine Optimization has evolved from speculative concept to established discipline with documented ROI, research-backed best practices, and a growing toolkit for implementation. The core insight from Princeton’s academic research—that specific, actionable content modifications can improve AI visibility by 40% or more—provides clear strategic direction.
The most successful strategies that integrate both traditional SEO and GEO approaches rely on both conventional search engines and AI-powered answer engines. Organizations that invest in GEO capabilities now—implementing technical requirements, building E-E-A-T signals, optimizing for platform-specific behaviors, and establishing measurement frameworks—will capture disproportionate value as AI search adoption accelerates.
The window for competitive advantage remains open but is narrowing as the discipline matures and adoption spreads. Organizations that establish AI visibility early build compounding advantages as AI systems develop trust relationships with consistent, authoritative sources.
The strategic imperative is clear: GEO represents both urgent opportunity and structural shift for digital marketing, and early movers will dominate their categories in the AI-first search landscape ahead.

